Paper is an essential component of everyday life all throughout the world. It is used for documentation, artistic expression, education, and communication. Its significance have not been impacted with introduction of new invention. Paper is still of a great importance.Let us explore “How paper is made” , one should understand that paper is plant product so utilisation of unnecessary will lead to environment impacts.As we know for making one tonn of paper we need 17 full grown trees.
Importance of paper
One of the easiest and most popular forms of written communication is still paper. Paper helps people, businesses, and institutions transmit information by facilitating handwritten letters and printed documents. Paper is a basic learning and knowledge-dissemination instrument in educational settings. Most educational resources, including worksheets, textbooks, and notebooks, are printed on paper and aid in the learning process from elementary school through higher education.
Documentation & Record-Keeping:
In both personal and professional settings, paper-based records are necessary for record-keeping needs. For legal validity reasons, official certificates, financial records, medical reports, and legal papers are frequently kept on paper.
Paper is a versatile material used by artists and creators to convey thoughts, feelings, and artistic visions. Paper allows for countless creative and artistic exploration options, from painting and sketching to origami and collage.
Packaging & Shipping:
Paper-based materials play a major role in the packaging industry’s ability to package and ship a wide range of commodities and products. While reducing their environmental impact, cardboard boxes, paper bags, and packing materials provide the safe transit and delivery of goods.
Marketing and Advertising:
A vital part of marketing and promotion campaigns for companies, goods, and services is the use of paper-based promotional materials including magazines, flyers, brochures, and posters. Printed ads promote brand awareness and recognition by reaching a variety of audiences.Paper has both personal and cultural value in customs, ceremonies, and rituals, in addition to its practical uses. Greeting cards, invites, and official paperwork are treasured mementos that mark important events and achievements.Paper is essential to daily life because it symbolizes human communication, creativity, and cultural expression in a way that goes beyond its material form. Paper still has value and is necessary in today’s world, even with the development of digital technologies.
History and Importance of paper making:
History : Paper making has a long history and rich cultural heritage that can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Egypt and China.
Paper Making is thought to have started in the Han Dynasty in ancient China, circa 100 BCE. Plant ingredients such as hemp fibers and mulberry bark were used to make traditional Chinese paper. The fibers had to be soaked, beaten, and pressed into thin sheets.By the eighth century, paper marking technology had traveled from China to the Islamic world via the Silk Road. Muslim intellectuals and artists in places like Damascus and Baghdad improved the procedure and added new features like watermark.The paper was produced in Europe, most likely as a result of the Moorish conquest of Spain. By the 12th century, paper mills were cropping up in Spain, Italy, and other European nations.
Process of paper Making( How paper is made)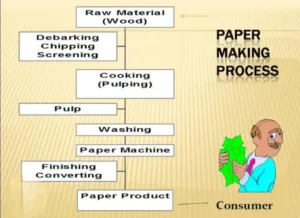
Main Ingredient:
Pulp Wood The majority of paper produced globally is made from wood pulp, which is the main raw material utilized in the process. It comes from a variety of tree species, including hardwood and softwood. To obtain wood pulp, a few steps must be completed:
Harvesting:
Trees chosen for pulp manufacture come from plantations or forests that are maintained sustainably. Because their long strands add strength to paper, softwood trees like spruce and pine are frequently employed.
Pulping:
The wood fibers in the harvested trees are broken down into a fibrous material called pulp via the pulping process. Mechanical, chemical, and semi-chemical processes are among the pulping techniques available; each gives the final pulp a unique set of properties.
Bleaching And Cleaning:
In order to get rid of lignin, hemicellulose, and other contaminants, the pulp is then put through bleaching and cleaning procedures. To get the proper color and brightness levels, bleaching chemicals such as hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, chlorine dioxide, and chlorine are utilized.
Forming: To create a continuous sheet of wet pulp, the cleaned pulp is combined with water to make a slurry, which is then placed onto a mesh screen or cylinder mold.
Pressing and Drying: In order to get the required thickness and eliminate extra water, the wet pulp sheet is pressed. To eliminate any leftover moisture and harden the paper sheet, it is subsequently dried using heated rollers or air drying techniques.
Recycling of paper And alternate sources
Recycled Paper:
By lowering the need for new fiber and cutting waste, recycled paper is becoming a more and more well-liked substitute for wood pulp. Recycled paper is produced by pulping, de-inking, and processing waste paper from the post-consumer or post-industrial sector in order to produce new paper goods. A paper can be recycled more 7 times.
Cotton:
Another alternate source of paper pulp is cotton fiber, which is obtained from cotton plants. Cotton paper is ideal for uses such as elegant stationery, cash, and archive documents because of its softness, durability, and archival quality.
Other Plant Fibers:
Hemp, bamboo, sugarcane bagasse, kenaf, and other plant fibers can all be used to make paper, in addition to wood and cotton. These fibers have special qualities and benefits for the environment, such as quick growth, high yield, and minimal environmental
Harvesting:
The process of harvesting trees and the varieties used to make paper.The trees chosen for paper making are taken from plantations or forests that are managed sustainably. The felling of trees and their transportation to the pulp mill are steps in the harvesting process.The soft wood trees are long, strong fibers, like fir, spruce, and pine are frequently used to make paper. For uses requiring sturdiness and strength, like packaging materials and printing paper, these woods are recommended. The hardwood Trees although are used less commonly than softwood trees, hardwood trees like eucalyptus, birch, and oak are also utilized to make paper. Because hardwood fibers are finer and shorter than softwood fibers, they can be used to produce smooth, superior papers that are utilized in printing
plup processing
The pulping process, in which wood fibers are extracted from lignin and other wood constituents to produce pulp, is an essential step in the manufacturing of paper. There are two main ways to pulp an object:
Mechanical Pulping:Using refiner plates or grinding stones, the wood logs are mechanically shredded or ground into tiny fibers during the mechanical pulping process.Pulp produced by this method has a large yield but a relatively low strength since the majority of the lignin in the wood is retained. Lower-grade paper goods and newsprint frequently employ mechanical pulp.
Pulping Chemicals:Chemical pulping is the process of dissolving lignin and separating the fibers from wood chips by treating them with chemicals.
Bleaching:
The bleaching process is an essential stage in the paper-making process that is used to get the required brightness and color of the paper by eliminating contaminants. This is a thorough rundown of the bleaching procedure.The pulp might go through a pre-bleaching procedure in order to get rid of extractives, lignin, and other impurities that could impede the bleaching process.Pre-bleaching procedures to increase the bleaching agents’ effectiveness could involve screening, washing, and chemical treatments.
Bleaching Substances:
Bleaching agents include hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and sodium hydrosulfite, among other substances.The choice of bleaching agent is contingent upon various criteria, including paper grade, environmental requirements, and desired brightness levels. Each bleaching agent has distinct qualities and applications.
Stages of Bleaching:
Usually, there are several steps in the bleaching process, each of which targets a different type of pollutant and produces progressively better brightness and color.Chlorine bleaching, alkaline extraction, hydrogen peroxide bleaching, hydrogen dioxide bleaching, and final brightness phases are examples of common bleaching steps.
Bleaching with Chlorine:
Although chlorine bleaching works well to remove lignin, it can also produce hazardous chlorinated organic compounds, which is why many mills are phased out of this process because of environmental concerns.Even yet, some mills continue to employ it when oxygen or chlorine dioxide delignification is impractical.other than chlore we can use hydrogen peroxide which less toxic to environment as it releases Oxygen as a byproduct.A bleaching agent that is safe for the environment. It is frequently applied in the last stages of bleaching to produce paper that is brilliant white.
Chlorine Dioxide Discoloration:When it comes to bleaching agents, chlorine dioxide is less harmful to the environment than chlorine. It minimizes harm to cellulose fibers while eliminating lignin with extreme selectivity.
Cleaning:
To get rid of any remaining bleaching agents, reaction byproducts, and dissolved and suspended contaminants, the bleached pulp is repeatedly washed with water.Washing can be done with a variety of tools, including centrifugal cleaners, washers, and screens.
Examining:Screening is the process of removing large particles, trash, and knots from pulp by running it through screens with different mesh sizes.Prior to being further processed into paper, this technique helps the pulp become more uniform and of higher quality.When it comes to recycled paper, the pulp could go through de-inking procedures to get rid of impurities, coatings, and ink from the recycled fibers.De-inkking is the process of separating ink particles from pulp fibers using chemical treatments, flotation, and washing.
Making of slurry :
The production of paper is based on the process of making a slurry from pulp and water, which is an essential stage in the paper-making process. This is how it usually operates.The pulp is usually kept in sizable tanks or chests, for the feature process. It could go through additional blending or refining to get the consistency and fiber properties that are needed.To make a slurry with the appropriate fiber content and consistency, the pulp is combined with water in a predetermined ratio.Water is progressively added to the pulp while stirring the mixture to guarantee that the fibers are distributed uniformly and to avoid clumping.
Based on the particular needs of the paper grade and production process, the pulp slurry’s consistency—which is expressed as the proportion of solid fibers in the mixture—is modified.Paper sheets with a higher consistency level are thicker than those with a lower consistency level.In certain instances, the pulp slurry may be supplemented with fillers, sizing agents, and dyes to improve the strength, smoothness, and color of the paper.To guarantee that the fibers and additives are evenly distributed throughout the mixture, the pulp slurry is vigorously combined and stirred.Agitation can be accomplished by means of mechanical stirrers, pumps, or agitators in order to preserve homogeneity and avert fiber settling.
Quality Assurance:
To guarantee the appropriate paper quality and performance, quality control procedures are used to keep an eye on the consistency, fiber distribution, and other factors throughout the mixing process.To make a continuous sheet of wet paper, the pulp slurry is deposited onto a forming surface during the paper creation process.
Machine processing
Water is further drained through suction boxes as the pulp moves along the wire, and the paper sheet passes through pressing and drying phases to remove extra moisture and harden the sheet.Vats or cylinder machines, sometimes referred to as cylinder molds, are utilized in the small- or specialty paper-making industries.The pulp slurry is deposited onto a revolving cylindrical mesh screen in a water-filled vat using cylinder mold machines.The wet paper sheet forms on the cylinder’s surface as water drains through the mesh while the cylinder rotates.After that, the produced sheet is moved to a felt conveyor belt where it is put through additional pressing and drying steps to create the finished paper product.
Thickness and drying
The paper sheet is formed with a lot of water in it, which needs to be pressed out to have the right consistency and thickness. The purpose of pressing, a crucial stage in the production of paper, is to remove extra water from the fibers and combine them into a compact, consistent sheet. The pressing procedure operates as follows:
Section for Press:
After passing through the shaping part, the paper sheet enters the press section of the machine, where it is pressed between pressing felts or heavy rollers.To progressively compress the paper sheet and remove extra water, the press section usually comprises of many sets of rollers stacked in a sequence.
Felted Presses:
During pressing, felts made of wool or synthetic materials are used to absorb water from the paper sheet and apply consistent pressure.The paper sheet is moved between felted blankets and rollers, which apply pressure to the sheet and help remove water.The Nip pressure is regulate and ensures efficient water drainage without causing damage to the paper fibers.More water removal may be possible with higher nip pressures, but there is also a chance of paper deformation or fiber damage.Several Pressing Stages:To maximize water removal and produce the required paper qualities, paper machines may have many pressing stages, each with a distinct nip pressure and arrangement.
Drying process
The paper sheet is dried again after pressing in order to eliminate any residual moisture and make the sheet firm enough for subsequent processing.The method of drying using heated rollers or air drying.The paper sheet is dried to obtain the desired moisture content and characteristics after any extra water is eliminated by pressing. Depending on the paper grade and production needs, either air drying or heated rollers can be used to complete the drying process:
Air-Drying:
The process of air drying entails putting the paper sheet through several conveyor belts or drying cylinders that are open to the surrounding air.The paper surface becomes dry as a result of the warm, moving air evaporating moisture, bringing the sheet closer to the appropriate moisture content.Air drying is an economical technique that works well for less time-sensitive production operations and lower-grade papers.
Warm Rollers:
The paper sheet is dried faster by passing it through a succession of heated rollers or cylinders that apply regulated heat and pressure. This technique is known as heated roller drying.Shorter drying times and higher production rates are made possible by the heated rollers’ speedier ability to remove moisture from the paper sheet.Time-sensitive production schedules, specialty grades, and high-quality sheets are among the applications for heated roller drying.
Steam Pumps:In some paper machines, additional heat for drying is provided by steam cylinders in addition to heated rollers.Consistent temperature and humidity levels are maintained by steam cylinders, which guarantees even drying and inhibits paper flaws like curling or wrinkling.
The proper moisture content of the paper is attained by monitoring and regulating moisture levels during the drying process. This affects the paper’s strength, smoothness, and dimensional stability.Paper makers may produce high-quality paper products with precise thickness, moisture content, and performance characteristics to fulfill the various needs of customers and industries by carefully managing the pressing and drying steps.
Surface smoothing:
An extra process called calendaring is used on paper to improve its gloss, printability, and smoothness of the surface. The paper sheet is passed between extremely polished rollers during the calendaring process, which is done at a controlled temperature and pressure. This is how a calendar functions.
Calendar Rolls:Rolls that alternate between being soft and firm are stacked in calendering machines.The soft rolls, which offer flexibility and even pressure distribution, might be composed of rubber or compressed paper. The hard rolls are composed of metal and have a polished surface.The paper sheet moves between the rolls, it is exposed to intense pressure and heat produced by friction from the rolling contact.
Cutting and packaging
The paper goes through cutting and packaging procedures in order to be distributed and sold once it has been produced and treated in accordance with the required criteria. An outline of the packaging and cutting procedures is provided below:
Rolling or Sheeting:
During the sheeting process, guillotine cutters or cutting machines are used to split big paper rolls into smaller sheets with predetermined dimensions.As an alternative, the paper is twisted into parent rolls—large rolls—during the reeling process, and these rolls are subsequently divided into smaller rolls for distribution.
Cutting and Sealing:
Paper rolls or sheets that have been cut may go through finishing and trimming procedures to get rid of any flaws, extra material, or uneven edges.Machines for trimming make sure the finished product satisfies customer requirements and quality standards.
Packaging:
After the paper is prepared and cut, it is packaged for sale and distribution into rolls, reams, or bundles.Depending on the paper grade and packaging specifications, packaging materials can be cardboard boxes, plastic wrap, or paper wrappers.
Barcoding and Labeling:
Paper goods are frequently barcoded and tagged for tracking, inventory control, and identification.Labels make it easier to identify and handle paper products by giving details about their maker, size, weight, and grade.Quality Assurance:Quality control procedures are used during the cutting and packaging stages to guarantee that the paper products fulfill requirements for dimensions, weight, moisture content, and other characteristics.
Environmental issues Related to paper production:
Deforestation:
Because wood pulp from forests is a major component of traditional paper production, there is a loss of wildlife habitat and deforestation. Unsustainable logging methods have the potential to upset ecosystems and accelerate the extinction of species.
Water Consumption:
The pulping, washing, and processing steps in the paper-making process need a lot of water. Excessive water use can harm nearby ecosystems and water sources, resulting in pollution and water shortages.
Chemical pollution:
Chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and hydrogen peroxide are among the chemicals used in the pulping and bleaching processes. When these chemicals are released into soil and waterways, they can cause harm to aquatic life and ecosystems.
Energy Use:
Paper mills use a lot of energy, mostly from fossil fuels, which increases greenhouse gas emissions and the effects of climate change. Transportation, drying, and pulping are examples of energy-intensive activities that worsen environmental effects.
Waste Generation: The process of making paper produces a variety of wastes, such as solid waste, wastewater, and pulping residues. When these waste streams are improperly disposed of, dangers to the environment and public health arise from contaminated land, water, and air.
How to minimise environment concerns:
Sustainable Forestry Methods:
Ensuring the long-term health and productivity of forests can be achieved by implementing sustainable forestry practices, such as responsible tree harvesting, reforestation, and participation in forest certification programs like FSC and PEFC.
Recycling and the Circular Economy:
By encouraging the recycling of paper and the use of recycled fibers, waste that ends up in landfills is reduced and the need for virgin wood pulp is lessened. Promoting a circular economy strategy aids in resource conservation and lessens environmental impact.
Alternate Fiber Sources:
To diversify the raw material base and lessen the strain on forests, consider investigating alternate fiber sources such agricultural waste, non-wood fibers (like hemp and bamboo), and agricultural wastes.Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in the paper-making process can be decreased by using cogeneration systems, energy-efficient technology, and process optimization.
Water Conservation: Reusing process water, cleaning wastewater prior to discharge, and putting conservation measures into place all assist reduce water use and pollution in paper mills.
Chemical Substitution and Reduction:
To lessen chemical pollution and its negative effects on the environment, ecologically friendly bleaching agents should be used, together with closed-loop systems for chemical recovery and reuse.Standards and Certifications: Acquiring certifications from organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) guarantees that paper products are produced from sustainably managed forests and satisfy strict social and environmental requirements.
Summary:
The Process of paper making and Its Importance .There are various steps that explains how paper is made the process of creating paper:Selection of Raw Materials: Raw materials include wood pulp, cotton, recycled paper, and other plant fibers.Pulping: Wood pulps are processed mechanically, chemically, or semi-chemically to remove lignin and other contaminants.Bleaching and Cleaning: In order to attain the appropriate brightness and cleanliness, the pulp is cleaned and bleached to get rid of contaminants.Paper Formation: Using devices such as the Fourdrinier machine or cylinder molds, the pulp is combined with water to make a slurry that is subsequently shaped into a continuous sheet.
Pressing and Drying: The paper sheet is pressed to remove excess water, then either air drying or heated rollers are used to dry the sheet.Extra Treatments: To improve printability and smooth the paper surface, calendaring and finally we came to know how paper is made

